Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Clinical Study
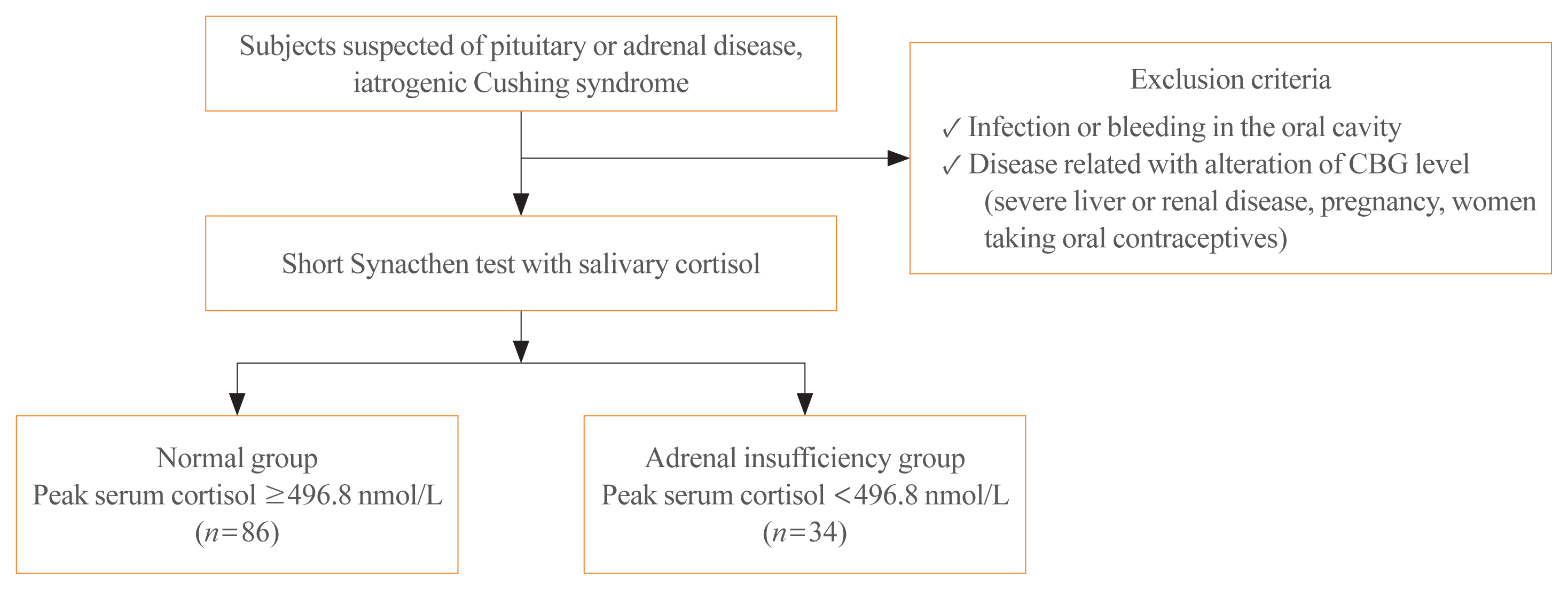
- Stimulated Salivary Cortisol as a Noninvasive Diagnostic Tool for Adrenal Insufficiency
- Yoon Ji Kim, Jung Hee Kim, A Ram Hong, Kyeong Seon Park, Sang Wan Kim, Chan Soo Shin, Seong Yeon Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(3):628-635. Published online September 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.707
- 5,848 View
- 202 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Salivary cortisol is routinely used as a diagnostic test for Cushing syndrome. The diagnostic use of salivary cortisol for adrenal insufficiency (AI), however, is less established. We aimed to investigate the utility of morning basal and adrenocorticotropic hormone-stimulated salivary cortisol in diagnosing AI in Korean adults.
Methods
We prospectively included 120 subjects (female, n=70) from Seoul National University Hospital. AI was defined as a stimulated serum cortisol level of <496.8 nmol/L during the short Synacthen test (SST). Serum and saliva samples were drawn between 8:00 AM and 10:00 AM. Salivary cortisol levels were measured using an enzyme immunoassay kit.
Results
Thirty-four patients were diagnosed with AI according to the SST results. Age, sex, body mass index, serum albumin levels, and serum creatinine levels did not significantly differ between the normal and AI groups. Basal and stimulated salivary cortisol levels were positively correlated with basal (r=0.538) and stimulated serum cortisol levels (r=0.750), respectively (all P<0.001). Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis yielded a cutoff level of morning basal salivary cortisol of 3.2 nmol/L (sensitivity, 84.9%; specificity, 73.5%; area under the curve [AUC]=0.822). The optimal cutoff value of stimulated salivary cortisol was 13.2 nmol/L (sensitivity, 90.7%; specificity, 94.1%; AUC=0.959). Subjects with a stimulated salivary cortisol level above 13.2 nmol/L but a stimulated serum cortisol level below 496.8 nmol/L (n=2) had lower serum albumin levels than those showing a concordant response.
Conclusion
The diagnostic performance of stimulated salivary cortisol measurements after the SST was comparable to serum cortisol measurements for diagnosing AI. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Extensive expertise in endocrinology: adrenal crisis in assisted reproduction and pregnancy
Ulla Feldt-Rasmussen
European Journal of Endocrinology.2024; 190(1): R10. CrossRef - Turning Antibodies into Ratiometric Bioluminescent Sensors for Competition-Based Homogeneous Immunoassays
Eva A. van Aalen, Joep J. J. Lurvink, Leandra Vermeulen, Benice van Gerven, Yan Ni, Remco Arts, Maarten Merkx
ACS Sensors.2024; 9(3): 1401. CrossRef - A Contemporary Approach to the Diagnosis and Management of Adrenal Insufficiency
Suranut Charoensri, Richard J. Auchus
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024; 39(1): 73. CrossRef - Diagnostic strategies in adrenal insufficiency
Vasiliki Siampanopoulou, Elisavet Tasouli, Anna Angelousi
Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes & Obesity.2023; 30(3): 141. CrossRef - The association between neuropeptide oxytocin and neuropsychiatric disorders after orthopedic surgery stress in older patients
Wanru Dong, Zengbo Ding, Xiao Wu, Ran Wan, Ying Liu, Liubao Pei, Weili Zhu
BMC Geriatrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Reliability of Salivary Cortisol Compared to Serum Cortisol for Diagnosing Adrenal Insufficiency with the Gold Standard ACTH Stimulation Test in Children
Silvia Ciancia, Sjoerd A. A. van den Berg, Erica L. T. van den Akker
Children.2023; 10(9): 1569. CrossRef - РІВЕНЬ СТРЕСУ В ДІТЕЙ ШКІЛЬНОГО ВІКУ З COVID-19
Г. А. Павлишин, О. І. Панченко
Здобутки клінічної і експериментальної медицини.2023; (4): 119. CrossRef - Secondary adrenal suppression related to high doses of inhaled corticosteroids in patients with severe asthma
Mariana Lobato, João Gaspar-Marques, Pedro Carreiro-Martins, Paula Leiria-Pinto
Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology.2022; 128(4): 464. CrossRef - Clinical and Technical Aspects in Free Cortisol Measurement
Man Ho Choi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(4): 599. CrossRef - Continuous biomarker monitoring with single molecule resolution by measuring free particle motion
Alissa D. Buskermolen, Yu-Ting Lin, Laura van Smeden, Rik B. van Haaften, Junhong Yan, Khulan Sergelen, Arthur M. de Jong, Menno W. J. Prins
Nature Communications.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Reversible Immunosensor for the Continuous Monitoring of Cortisol in Blood Plasma Sampled with Microdialysis
Laura van Smeden, Annet Saris, Khulan Sergelen, Arthur M. de Jong, Junhong Yan, Menno W. J. Prins
ACS Sensors.2022; 7(10): 3041. CrossRef - Adrenal insufficiency in HIV/AIDS: a review
Simon Mifsud, Zachary Gauci, Mark Gruppetta, Charles Mallia Azzopardi, Stephen Fava
Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism.2021; 16(6): 351. CrossRef
- Extensive expertise in endocrinology: adrenal crisis in assisted reproduction and pregnancy

- The Localization of Microadenoma with Sella Imaging Study and Inferior Petrosal Sinus Sampling in Cushing's Disease.
- Jae Seok Jeon, Sang Jeon Choi, Chan Soo Shin, Kyoung Soo Park, Seong Yeon Kim, Bo Youn Cho, Hong Kyu Lee, Chang Soon Koh, Hee Won Jung, Dae Hee Han, Moon Hee Han, Kee Hyun Chang
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1996;11(4):492-499. Published online November 7, 2019
- 1,016 View
- 21 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Inferior petrosal sinus sampling(IPSS) is known to be useful for the differential diagnosis of ACTH-dependent Cushings syndrome and for the preoperative lateralization of pituitary microadenoma. We tried to analyze the relative value of IPSS in localization of microadenoma as compared with sella imaging study including computerized tomogram(CT) or magnet resonance imaging(MRI) in Cushings disease. Methods: We reviewed the clinical records of 21 patients with Cushings disease who underwent IPSS and the radiologic study such as sella CT or sella MRI preoperatively followed by transsphenoidal microsurgery. By pathologic examination including immunohistochemistry and postoperative clinical and biochemical evaluation we confirmed the diagnosis of Cushings disease due to pituitary microadenoma in all 21 cases. Results: Sella CT or sella MRI detected microadenoma in 57.1% of cases( =12/21), while recently available dynamic MRI did so in 7 out of S cases. With IPSS the diagnosis of Cushings disease was possible in 90.5% of cases(= 19/21), but accurate lateralization of microadenoma was achieved in only 63.2% of cases( =12/19). IPSS precisely localized the pituitary microadenoma in 6 out of 9 cases whose lesion were not detected by the radiologic study. Of 7 cases in which IPSS failed to localize microadenoma, the radiologic study detected the lesion in 6 cases. Of 5 cases in which IPSS and the radiologic study showed a discrepancy in location of microadenoma, the radiologic study correctly localizaed the lesion in 4 cases and IPSS did so in one case. Conclusion: IPSS is not more reliable than sella imaging study for preoperative localization of microadenoma in Cushings disease. However it might have a complementary role, especially when sella imaging study failed to visualize the lesion.

- The Incidence of Thyroid Autoantibody in Subacute Thyroiditis and the Clinical Characteristics of Greeping Thyroiditis.
- Jae Seok Jeon, Won Bae Kim, Hae Young Park, Young Joo Park, Hyun Kyung Chung, Sang Jeon Choi, Chan Soo Shin, Kyoung Soo Park, Seong Yeon Kim, Bo Youn Cho, Hong Kyu Lee, Chang Soon Koh
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1996;11(4):438-446. Published online November 7, 2019
- 1,264 View
- 30 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Subacute thyroiditis is a spontaneously resolving inflammatory disorder of thyroid gland, usually associated with painful goiter and short-lived thyrotoxicosis. Although its etiology is yet to be established, much evidence suggests viral infections and genetic factors play important roles. Usually, both lobes of thyroid gland are involved simultaneously, but in some patients one lobe is involved first and the other later(creeping thyroiditis), Thyroid autoantibodies which might appear probably due to inflammatory release of thyroid antigens, are found in a variable number of patients with subacute thyroiditis. However there have been few detailed reports on their incidence in Korean patients with subacute thyroiditis. So, we were to see the elinical characteristics of patients with subacute thyroiditis with special regards to the incidence of thyroid autoantibodies and to the incidence and characteristics of creeping thyroiditis, Methods: We reviewed the clinical records of 85 patients with subacute thyroiditis(7 men and 78 wornen, meam age of 43+9 years) who had visited the thyroid clinic in Seoul National University Hospital between 1986 and 1994. Results: At initial visit, the incidenees of thyroid autoantibodies were as follows: anti- microsomal antibody 7.8%, anti-thyroglobulin antibody 22.1%, and thyratropin binding inhibitor inununglobulin 6.3%. During the follow-up period, thyroid autoantibodies appeared most frequently between the first and the second month after initial visit. Compared to those with non-creeping thyroiditis, the patients with creeping thyroiditis(21.4%) had nonspecific systemic sy~rnptoms more frequently(89% vs. 42%, p<0.05). They required steroid therapy more ftequently(89% vs. 52%, p <0.05), and needed longer duration of treatment(9.3+6.2weeks vs, 4.7+3.7weeks, p<0.05). The incidence of abnormalities in liver function and the incidence of thyroid autoantibodies were higher in non-creeping thyroiditis group. Conclusion: In accordance with previous reports, thyroid autoantibodies were detected in only a small portion of Korean patients with subacute thyroiditis. Rather different clinical manifestations and different incidences of thyroid autoantibodies between ereeping group and non-creeping group suggest differences in the pathogenetic mechanisms between those two groups. However, there is need for further study to validate such observation and to elucidate the mechanisms.

- A Clinical Study on Hypopitutiarism: Significance of Combined Pituitary Stimulation Test.
- Bo Youn Cho, Hong Gyu Lee, Chang Soon Koh, Hyung Kyu Park, Sook Kyung Kim, Chan Soo Shin, Seong Yeon Kim, Jae Seok Chun, Kyung Soo Park, Hyeon Kyu Kim, Sun Wook Kim
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1996;11(3):268-276. Published online November 7, 2019
- 1,237 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Hypopituitarism can be caused by various diseases. Its clinical manifestations vary, depending on the extent and severity of the pituitary hormone deficiency. And some patients may initially present with SIADH-like features. Combined pituitary stimulation test has been used for the diagnosis of hypopituitarism and subsequent hormone replacement therapy. However, the test is laborious, expensive and uncomfortable to the patients, So we performed this study to know whether combined pituitary stimulation test can be replaced with clinical features and simple basal hormone concentrations. Methods: Fifty-four patients who were diagnosed as hypopituitarism by combined pituitary stimulation test were included in this study. Clinical features and basal hormone data were compared with the results of combined pituitary stimulation test for the evaluation of pituitary-gonadal, pituitary-thyroid, and pituitary-adrenal axes, using X2 test. Results: 1) In pituitary-gonadal axis, the evaluation of clinical features and basal gonad hormone concentrations were significantly consistent with stimulation test(p<0.05), 2) In pituitary-thyroid axis, the evaluation of basal thyroid hormone concentrations were more helpful than stimulation test though results of the two tests were not consistent. 3) In pituitary-adrenal axis, all patients whose basal cortisol concentrations were low showed inadequate responses to stimulation test. However, stimulation test revealed adrenal insufficiency in some patients with normal basal cortisol concentrations. 4) 9 patients who presented with SIADH-like features were older than the others and had all corticotropin deficiency. Conclusion: In patients with suspected hypopituitarism, the evaluation of clinical features and basal hormone concentrations can be sufficient for the diagnosis of hypopituitarism and hormone replacement therapy. However, stimulation test is necessary to investigate adrenal function in patients with normal basal cortisol concentrations. And hypopituitarism should be considered in old patients who present with SIADH-like features.

Case Report
- A Case of Symptomatic Severe Hypercalcemia as Initial Manifestation of Hyperthyroidism.
- Hye Young Park, Won Bae Kim, Hyeon Kyu Kim, Chan Soo Shin, Seong Yeon Kim, Bo Youn Cho, Hong Gyu Lee, Chang Soon Koh
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1996;11(1):124-126. Published online November 7, 2019
- 1,108 View
- 20 Download

Original Articles
- Clinical Characteristics of Graves' Disease Patients with Undetectable Thyrotropin Binding Inhibitor Immunoglubulin (TB2).
- Bo Youn Cho, Won Bae Kim, Hong Gyu Lee, Chang Soon Koh, Seong Yeon Kim, Seok In Lee, Jae Seok Chun, Kyung Soo Park
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1996;11(1):68-74. Published online November 7, 2019
- 1,613 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Graves disease is an autoimmune disease caused by TSH receptor antibodies. Thyrotropin binding inhibitor immunoglobulins(TBII) are detected in most Graves patients, but some patients have no TBII activities in their sera. It is unknown whether the clinical features of TBII-positive patients are different from those of TBII-negative patients. Methods: To evaluate the prevalence of TBII-negative Graves' patients and its clinical differences from TBII-positive patients, we examined TBII by radioreceptor assay in 686 consecutive untreated Graves patients. We found 84 TBII-negative patients(15 men and 69 women, mean age ±EM: 40.9±.4 years) and compared their clinical characteristics with 87 TBII-positive patients (22 men and 65 women, mean age±EM: 39.9±.5 years) who were selected randomly from the same patients group. Results: In this study, TBII was undetectable in 12.2% of patients with Graves' disease(84 of 686). TBII-negative group had a less weight loss than TBII-positive group. However, there was no significant differences in age, sex ratio, prevalence of ophthalmopathy, duration of illness and positive rate of family history for thyroid diseases between TBII-negative and -positive groups. Serum total T or T levels were not different from each other, but T3-uptake was significantly higher in TBII-positive group than that in TBII-negative group, suggesting that the free hormone levels in TBII-negative group might be lower. The thyroid uptake of 99mTcO4 was significantly higher in TBII positive group than that in TBII-negative group. Thyroid autoantibodies, including antimicrosomal and antithyroglobulin antibodies were detected in almost all patients but there were no differences in titers and positive rate between TBII-negative and -positive groups. Conclusion: Although TBII-negative Graves patients showed less weight loss and low 99mTc04 thyroidal uptake compare to TBII-positive patients, the clinical and immunological characteristics of TBII-negative patients are not different from TBII-positive one.

- Changes in Serum Lipids and Apolipoproteins Levels According to the Thyroxine Treatment in The Patients with Subclinical Hypothyroidism.
- Hye Young Park, Bo Youn Cho, Won Bae Kim, Hong Gyu Lee, Chang Soon Koh, Geon Sang Park, Hyung Kyu Park, Sook Kyung Kim, Chan Soo Shin, Seong Yeon Kim
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1996;11(1):41-51. Published online November 7, 2019
- 1,221 View
- 21 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
Subclinical hypothyroidism(SCH) is a common biochemical abnormality which can be found in routine screening tests of thyroid function. We are increasingly faced with the question of whether its an indication for thyroxine replacement therapy. The effect of thyroxine replacement on lipid profile in SCH has aroused a great interest because of an association of overt hypothyroidism(OVH) with hyperlipidemia and increased risk of coronary artery disease. Method: We prospectively evaluated the changes in lipids and apoproteins before and after thyroxine replacement therapy in 23 patients with SCH and in 37 patients with OVH. We measured serum total cholesterol and triglyceride using autoanalyzer, high density lipoprotein(HDL) chole-sterol by dextran sulfate method, Apo A1 and Apo B by immunonephelometric assay. Results: Thyroxine replacement therapy significantly decreased total cholesterol, low density lipoprotein(LDL) cholesterol and apo B levels, but did not affect the level of triglyceride, HDL cholesterol or apo AI in patients with OVH. In SCH, thyroxine replacement therapy with the doses to normalize serum TSH concentrations also decreased significantly the level of cholesterol and LDL cholesterol albeit apo B levels did not change. Moreover, in most of patients with OVH (11 of 12) and in all of patients with SCH(5 of 5) who had had hyperchlesterolemia before treatment, thyroxine replament normalized their cholesterol and LDL cholesterol levels. Conclusion: In regard to the beneficial changes in blood lipid levels, patients with SCH should be treated, especially in cases who have other risk factors for the development of atherosclerosis. If thyroxine replacement only will reduce the incidence of coronary artery disease in SCH remains to be elucidated by long-term prospective studies.

- A Study on the Urinary Iodine Excretion in Normal subjects and Patients with Thyroid disease.
- Seong Yeon Kim, Bo Youn Cho, Hong Kyu Lee, Seok In Lee, Woon Bae Kim, Hye Young Park, Chang Soon Koh
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1995;10(4):386-394. Published online November 7, 2019
- 1,344 View
- 69 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - An adequate supply of dietary iodine is essential for the synthesis of the thyroid hormons. The measurement of dietary iodine intake is important for the clinical assessment of thyroid disease, especially in areas where iodine intake is excessive or deficient.To evaluate dietary iodine intake in Korean and its effects on thyroid function, we measured urinary iodine excretion with morning urine by electrode method in 184 normal subjects, 96 postpartum women and 181 patients with thyroid disease from October 1994 to February 1995. The results were as follows;1) In normal control, the mean value of urinary iodine excretion was 3.8+-2.7mg/L (range 0.1-15.0mg/L). However, there was no sex and age differences in the urinary iodine excretion.2) In postpartum women, the urinary iodine excretion was 9.0+-10.8mg/L who were not taken high iodine diet(Miyok-Guk), the mean value was statistically higher than normal control(p<0.01) and significant increased the urinary iodine excretion after eating of high iodine diet(p<0.01).3) In volunteer, there were increase of urinary iodine excretion more than 10 folds after high iodine diet and medication.4) The urinary iodine excretion in patients with thyroid diseases was not different from normal control, and there were no significant differences of urinary iodine excretion among the patient groups. The urinary iodine excretion in the acute stage of patients with subactue thyroiditis or painless thyroiditis was significantly increased compared to the recovery stage. However, it was not significantly different from that of normal control.In conclusion, urinary iodine excretion in Korean population is very high comparing to the reported data in Western population but similar with Japanese. The urinary iodine excretion is significant increase( more than 10-folds of basal level) after high iodine diet or high iodine containing medication in postpartum women or healthy persons. As a clue of destruction induced thyrotoxicosis, the urinary iodine excretion measurement is not valid in area where iodine intake is excessive like Korea.

- Relationship between Blood Pressure and Insulin Level or Red Cell Membrane Na+ Transport in Acromegaly.
- Seong Yeon Kim, Hyun Kyu Kim, Kyung Soo Park, Bo Youn Cho, Hong Kyu Lee, Chang Soon Koh
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1995;10(1):35-44. Published online November 6, 2019
- 1,092 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - To test the hypothesis that hyperinsulinemia and/or abnormalities of red cell membrane Na^+ transport are concerned in the pathogenesis of hypertension, we investigated the relationship between blood pressure, insulin level and red cell membrane Na^+ transport in patients with acromegaly which is frequently associated with hypertension, hyperinsulinemia and abnormalities of red cell membrane Na^+ transport.The results were as follows;1) BMI and both systolic and diastolic blood pressure were significantly higher in patients with acromegaly than in control subjects.2) Fasting glucose and insulin levels were higher, and both serum glucose and insulin responses after a 75g glucose load were significantly increased in patients with acromegaly as compared with control subjects.3) Vmax of Na^+-Li^+ countertransport were significantly higher in patients with acromegaly than in control subjects while red cell Na^+ concentration and Vmax of Na^+, K^+ ATPase were similar in the two groups.4) In multiple stepwise regression analysis, age was directly correlated with both systolic and diastolic blood pressure in acromegaly. On the other hand both insulin level and red cell membrane Na^+ transport showed little correlation with either systolic or diastolic pressure. 5) Prevalence of hypertension in acromegaly was 39%(9 out of 23) and only age except for blood pressure was significantly higher in hypertensive acromegalic patients than in normotensive acromegalic patients while GH level, insulin levels and red cell membrane Na^+ transport were similar in the two groupsThese results suggest that hyperinsulinemia or abnormalities of red cell membrane Na^+ transport are not causally related to hypertension in patients with acromegaly.

Case Report
- A Case of Thyroid Anaplastic Cancer with Intestinal Metastasis.
- Seong Yeon Kim, Kyung Soo Park, Bo Youn Cho, Hong Kyu Lee, Chang Soon Koh, Jae Seok Jeon, Min Seon Kim, Won Bae Kim
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;9(4):375-379. Published online November 6, 2019
- 1,163 View
- 23 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Thyroid anaplastic cancer is one of the most malignant neoplasms encountered in human. These tumors usually present as rapidly enlarging neck mass in old patients who may or may not have had a previously recognized goiter. The distant metastases of anaplastic cancer eventually occur in about 50% patients, mostly in the lung and bone and are an important prognostic factor, substantially reducing survival time.A 66-year old man visited out hospital because of rapidly growing anterior neck mass and hoarseness. He was diagnosed as thyroid anaplastic cancer with lymph node and lung metastasis and received combined chemotherapy and radiation therapy. On the 8th hospital day, severe abdominal pain developed and exploratory laparotomy was conducted. During operation, two intestinal mass were discovered, one of which was perforated. The microscopic examinations showed that undifferentiated malignant cells were infiltrated in the wall of small bowel. We report this case because we first experienced thyroid anaplastic cancer with intestinal metastasis.

Original Articles
- Insulin Resistance, Body Fat Distribution, and Sex Hormones in Healthy Men and Premenopausal Women.
- Seong Yeon Kim, Kyung Soo Park, Bo Youn Cho, Hong Kyu Lee, Chan Soo Shin, Chang Soon Koh, Tae Geun Oh, Woon Bae Kim
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;9(4):366-374. Published online November 6, 2019
- 1,197 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - It is well known that obesity central obesity is associated with insulin resistance and some studies reported that sex hormones were associated with insulin resistance. Recently, low levels of sex-hormone binding globulin(SHBG), an indirect index of androgenicity, have been observed to predict the development of non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus(NIDDM) in women and SHBG has been proposed as a marker for insulin resistance. In contrast to findings in women, decreased SHBG did not predict the occurrence of NIDDM in men, so it is suggested that sex hormones may have a different role for insulin resistance between men and women. To investigate the difference of the associations among the body fat distribution, sex hormone and insulin sensitivity index in men and women, we measured body-mass index(BMI) and waist to hip circumference ratio(WHR) and concentrations serum SHBG, total testosterone, free testosterone, and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate(DHEA-S) concentrations in 29 healthy adults(men:19, women:10) who showed normal glucose tolerance. Insulin sensitivity index(M/I) was measured by euglycemic hyperinsulinemic clamp. There were no differences in age, BMI, fasting plasma glucose, insulin and free fatty acid levels between men and women. WHR of men is higher than that of women(0.82+-0.01 vs. 0.73+-0.01, p=0.002). Insulin sensitivity index(M/I) is similar in men and women(7.80+-0.71 mg/kg/min/uU/ml X 100 vs. 9.74+-0.89 mg/kg/min/uU/ml X 100, p=0.196).In Pearson's correlation, M/I was significantly correlated with BMI(r=-0.69, p<0.01) and WHR(r=-0.68, p<0.01) in men and DHEA-S(r=-0.68, p<0.05) and SHBG(r=0.61, p=0.056) concentrations in women.In multiple regression analysis, M/I had the most significant association with BMI(R^2=0.484, beta=-0.696, p<0.001) in men and DHEA-S(R^2=0.471, beta=-0.686, p<0.05) concentration in women.Conclusively, we found that sex hormones were significantly associated with insulin resistance and the effects of sex hormones on insulin resistance may be different in men and women.

- Effect of Antiliyolytic Agents on Glueose Metabolism in Thyrotoxic Patients.
- Seong Yeon Kim, Kyung Soo Park, Bo Youn Cho, Hong Kyu Lee, Chan Soo Shin, Chang Soon Koh, Hun Ki Min, Tae Geun Oh, Chul Hee Kim, Moon Kyu Lee, Jong Ho Ahn, Kee Up Lee
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;9(4):325-331. Published online November 6, 2019
- 1,184 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Decreased glucose tolerance is often found in patients with thyrotoxicosis but the pathogenetic mechanisms are poorly understood. Since the concentrations of free fatty acid are usually elevated due to increased lipolysis in thyrotoxicosis, the preferential oxidation of the free fatty acids may explain the decreased glucose tolerance in hyperthyroidism. The aim of this study was to investigate whether lowering plasma free fatty acid(FFA) by acipimox, a long-acting antilipolytic agent, could affect glucose metabolism in thyrotoxicosis. We performed intravenous glucose tolerance test with acipimox or placebo in 6 untreated thyrotoxicmen and 6 age-and body mass index(BMI)-matched controls. The following results were obtained.1) The basal plasma FFA concentration in thyrotoxic patients were significantly higher than those in controls(997.0+-303.4 uEq/L vs. 290.5+-169.1 uEq/L; p<0.01). 2) Plasma FFA concentrations decreased rapidly with acipimox ingestion in both controls and thyrotoxic patients.3) Plasma glucose concentrations were significantly lower with acipimox ingestion than with placebo in thyrotoxic patients from 17min after intravenous glucose load and to the end of the study.4) Plasma insulin concentrations in thyrotoxic patients with acipimox ingestion were higher at 5, 7 min after iv glucose load.5) In thyrotoxic patients, glucose disappearance rate(K_glucose) in acipimox treatment was significantly higher than that in placebo treatment(2.44+-0.84 vs. 1.58+-0.37;p<0.05). 6) K_glucose values were inversely correlated with basal FFA concentrations(r=-0.58, p<0.05). In summary, in thyrotoxic patients with elevated plasma FFA levels, acipimox lowered plasma FFA, which in turn improved glucose tolerance.

- Changes in Thyrotropin Receptor Blocking Antibody after Antithyroid drug Administration to Patients with Atrophic Autoimmune Thyroiditis (Primary Myxedema).
- Seong Yeon Kim, Bo Youn Cho, Hong Kyu Lee, Jae Hoon Chung, Chang Soon Koh, Chan Soo Shin, Won Bae Kim
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;10(3):229-241. Published online November 6, 2019
- 1,067 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - It is well Known that antithyroid drug treatment of Graves' disease suppresses excessive thyroid hormone synthesis and causes a parallel decrease in serum thyroid autoantibody levels including thyroid stimulating antibodies(TSAb) in most patients suggesting the immunosuppressive or immunomodulating effects of antithyroid drugs. In the context of view that thyrotropin receptor blocking antibody may play an important pathogenetic role at least in some patients with primary myxedema(chronic atrophic autoimmune thyroiditis), antithyroid drug treatment in these patients might be beneficial to disease course. To evaluate the effect of antithyroid drug on the thyrotropin receptor blocking antibody levels, we serially measured thyrotropin-binding inhibitor immunoglobulins(TBII) and thyroid stimulation blocking antibodies(TSBAb) using FRTL-5 cells, antimicrosomal- and antithyroglobulin antibody activities in 7 patients with primary myedema who have blocking TSH receptor antibodies during 6 months of methimazole(MMI, 40mg/day) administration. TBII and TSBAb activities did not change after MMI, but one of them showed stepwise decrease and disappearance of TBII and TSBAb activities. Antimicrosomal- and antithyroglobulin antibody activities decreased significantly after 3 months of MMI administration in those patients. These results suggest a minimal effect of antithyroid drug treatment on the level of thyrotropin receptor blocking antibodies. Persistence of thyrotropin receptor blocking antibodies despite of the decrease in antimicrosomal and antithyroglobulin antibodies might suggest that blocking TSH receptor antibodies of primary myxedema is produced mainly in extrathyroidal tissue in contrast to the thyroid stimulating antibodies of Graves' disease. One patient, whose blocking antibody have disappeared after MMI treatment, is under observation to see if she will remain in remission of hypothyroidism.

Case Report
- A Case of Thyrotropin - Secreting Pituitary Adenoma.
- Seong Yeon Kim, Bo Youn Cho, Hong Kyu Lee, Chang Soon Koh, Woon Bae Kim, Hye Young Park, Jin Sung Kim
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;10(2):153-160. Published online November 6, 2019
- 1,246 View
- 21 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - thyrotropin-secreting(TSH) pituitary adenoma is extremely rare condition causing hyperthyroidism by uncontrolled secretion of thyrotropin. Among total pituitary adenomas, less than 1 percent are thyrotropin-secreting type, and only about 150 cases have been reported till now. However, increasing numbers of cases are being found due to the availability of ultra-sensitive TSH assay. We report here a patient with thyrotropin-secreting pituitay adenoma secreting TSH with production of lutenizing hormone(LH), follicle stimulating hormone(FSH), growth hormone(GH), prolactin(PRL) and free alpha-subunit.A 21-years old man visited thyroid clinic because of palpitation and dyspnea on exertion. He had diffuse goiter and features of mild thyrotoxicosis, and his thyroid function test showed increased T3, T4 and normal TSH. Serum free alpha-subunit concentration was 7420.5pg/ml(24.7mIU/ml) and the molar ratio of free alpha-subunit to TSH was 15.9. Basal pituitary hormone levels except TSH and the response to combined pituitary stimulation test were normal. A large sellar mass extending into frontal lobe was found on sellar MRI, so it was removed surgically leaving residual tumor mass due to the extensive nature of tumor. In immunohistochemical study the tumor tissue was stained with antibodies to TSH, LH, FSH, GH and PRL. His hyperthyroidism and goiter disappeared after partial removal of tumor. Somatostatin analogue(octreotide acetate) were given continuously via subcutaneous route(150 ug/day) using infusion pump to reduce the size of residual tumor. After 4 months of octreotide infusion, the size of tumor decreased slightly, and he is under treatment without any side effect.

Original Article
- A Clinical study on the diagnesis and Treatment of Cushing's Disease - The significance of bilateral inferior petrosal sinus sampling -.
- Seong Yeon Kim, Kyung Soo Park, Bo Youn Cho, Hong Kyu Lee, Jae Seok Jeon, Hyeong Kyu Park, Chang Soon Koh, Hun Ki Min, Heu Won Jeong, Dae Hee Han, Moon Hee Han, Kee Hyun Jang
- J Korean Endocr Soc. 1994;9(2):115-120. Published online November 6, 2019
- 1,094 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Bilateral inferior petrosal sinus sampling(IPSS) is known to be useful for the differential diagnosis of ACTH-dependent Cushing's syndrome and for the preoperative localization of pituitary microadenomas.To evaluate the usefulness of IPSS, we performed the procedure in the 17 cases of ACTH-dependent Cushing's syndrome including 2 cases of macroadenomas, 6 of them with CRH stimulation test. A inferior petrosal sinus-to-peripheral ACTH ratio of 2:1 or greater(3:1 after CRH stimulation) indicates a pituitary source of ACTH hypersecretion, and a ratio of the ACTH level in one inferior petrosal sinus to the ACTH level in the other of 1:4 or greater lateralizes the microadenomas to that half of the pituitary gland.With these criteria, we diagnosed Cushing's disease in 15 of 17 cases of ACTH-dependent Cushing's syndrome, and localized the lesion in 8 of 13 cases of microadenoma.In conclusion, IPSS with CRH stimulation has high diagnostic accuracy in the differential diagnosis of ACTH-dependent Cushing's syndrome, but still has the limitations on the localization of microadenoma.


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



